As per Forbes, there are 8.93 million mobile apps available worldwide. However, all of them are successful well. The answer is an obvious no. Tell me, how many mobile apps do you know of? WhatsApp, Instagram, Uber, and a few others you use daily for work or leisure.
So, what about the other millions? All of them are flops! Again no. A mobile app with an effective 500+ downloads every day is considered successful. Moreover, there are tons of other parameters.
Nearly 4000 apps are released every day, and most of them fail to woo the customer. Among multiple factors determining the success of an app, choosing the deployment platform with an effective marketing strategy plays a crucial role.
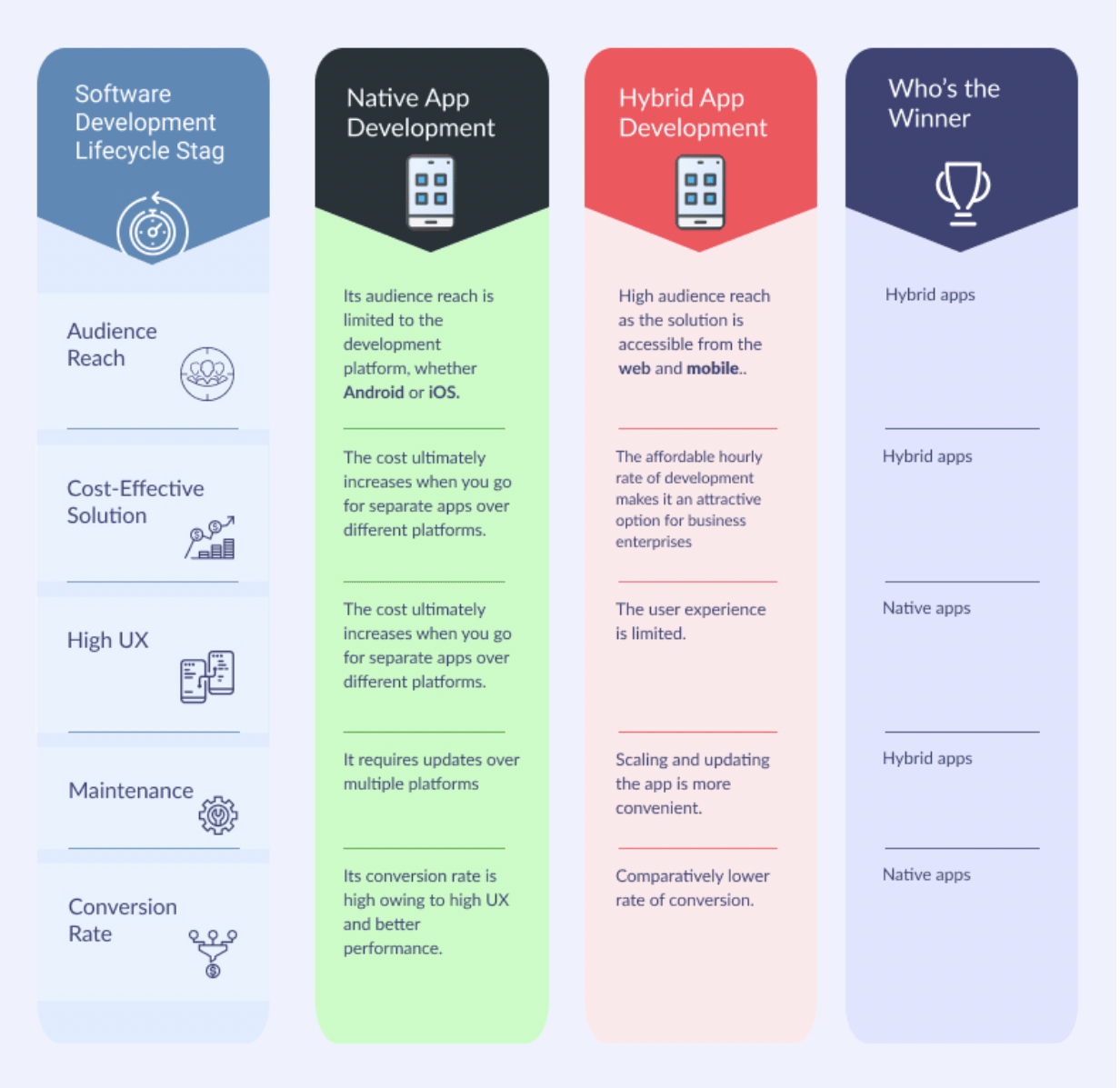
Businesses typically have 2 options when developing mobile apps: native and hybrid. Each one has its benefits and drawbacks, so choosing the right one for your business needs and customer expectations is essential. Find out how these two approaches differ from the table below & how you can select the best one for your app development process!
Comparison Table: Native vs. Hybrid Mobile Apps
Hopefully, the above table gives you a concise idea of what suits your programming project and effectively explains the difference between a native and hybrid app. Let’s explore each of them in detail to analyze the better option between Native vs. Hybrid Mobile Apps.
We will cover the following:
- What is Native app development?
- Pros and cons of Native app development.
- What is Hybrid app development?
- Pros and cons of Hybrid app development?
- Native vs. Hybrid Mobile Apps: Which one offers a high audience reach?
- Native vs. Hybrid Mobile Apps: Which one is a cost-effective solution?
- Hybrid vs. Native Mobile Apps: Which one provides an elevated user experience?
Let us cover them in detail.
1) What is Native Mobile App Development?
A native app is an application that runs directly on a mobile device. It uses device-specific code (sometimes called machine code) instead of code that any device can understand.
It means that it needs to be coded explicitly for each platform where it will run, so developers need to create different apps if they want their app to run on iOS, Android, Blackberry, etc.
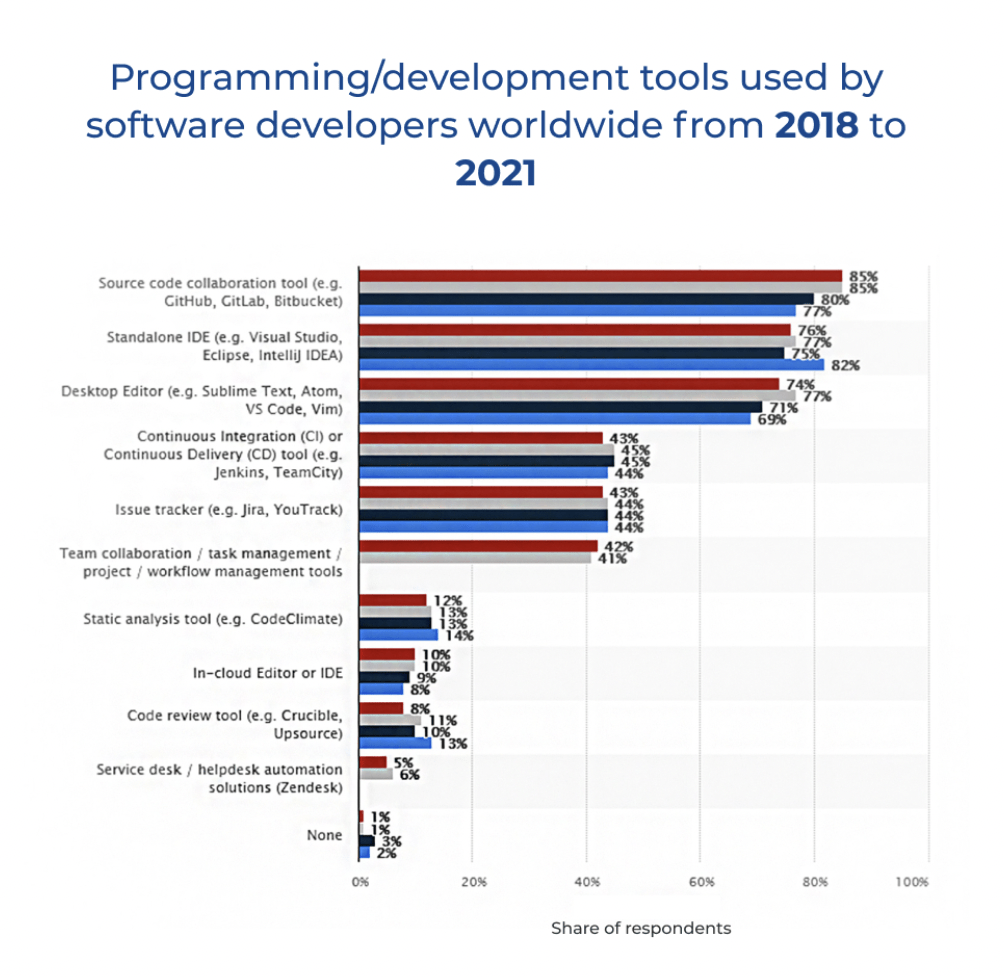
Do you know the top tools used by software developers worldwide?
The infographic below offers insights into the top tools used by developers worldwide.
An advantage of native apps is that they take advantage of hardware-specific features (e.g., GPS or camera). If a website has multiple interfaces for different platforms, then one might say that it is a multi-platform app rather than a native app.
Let’s explore the pros and cons of Native mobile apps.
Benefits of Native Mobile App Development:
- Design: It’s easier to design an app that matches an individual company’s brand when you can tailor it specifically for that company.
- Open-source licensing fees: If you are looking to build a popular app, there’s a good chance it’ll be open source, and those apps can cost thousands (or even millions) per year in licensing fees if built from scratch using open source. With a native app, your company won’t have to worry about paying for that.
- Upfront or maintenance costs: Native apps are typically cheaper to develop upfront because they come with existing frameworks and infrastructure rather than requiring developers to start entirely from scratch.
- High security: Unlike web apps (which often run locally on users’ devices), native apps run in an isolated environment called an app container that limits access to devise data such as camera functions and location information. It ultimately makes the app more secure for the users.
- Offers high app performance: When apps are first launched, they are often unoptimized—meaning they don’t run as smoothly as possible. That can be especially bad for devices with older hardware built before native apps even existed.
- High UX: While native apps can be more expensive in terms of time, labor and maintenance costs, they typically offer a more intuitive user experience that makes it easier for users to access your app’s core features. Ultimately, if you want to give users a powerful experience, a native app may be your best bet.
- Long-term maintenance: Maintaining web apps can get costly, primarily when multiple developers work on an app with high traffic or usage. Native apps get usually developed by one development team, which often means less work overtime for updates and changes.
Drawbacks of Native Mobile App Development:
- End-user functionality: If you are building a native app, there is a good chance it will have all sorts of bells and whistles (and likely, multiple iterations) before being ready for market. It can cost a pretty penny in both development time and staffing needs. On top of all that, once an outside firm builds an app, your company has little control over updates and ongoing tweaks, which can ultimately lead to higher maintenance costs down the road if they require input from multiple parties.
- No fixed cost: Development costs and time can vary significantly depending on development tools (or languages), design, scope, and schedule. For those reasons, it’s essential to consider all aspects when comparing developing costs for web vs. native apps.
2) What is Hybrid Mobile App Development?
What exactly is hybrid mobile app development? The term itself is a bit nebulous. Some describe it as a native app plus Web or the best of both worlds. However, there’s no one standard definition for hybrid apps. However, a hybrid app relies on some native code (e.g., HTML5) that serves as a foundation upon which you can layer native functionality (e.g., UI components).
For example, you might begin with an HTML5/CSS3 user interface and then add Cordova plug-ins to access device capabilities like location information or camera access. A hybrid app is essentially a mix between a native mobile app and a web app.
So, when you hear that someone has developed a hybrid mobile app, they say that the developers took some HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or another similar language (in tandem with native device functionality) to create an application for multiple platforms.
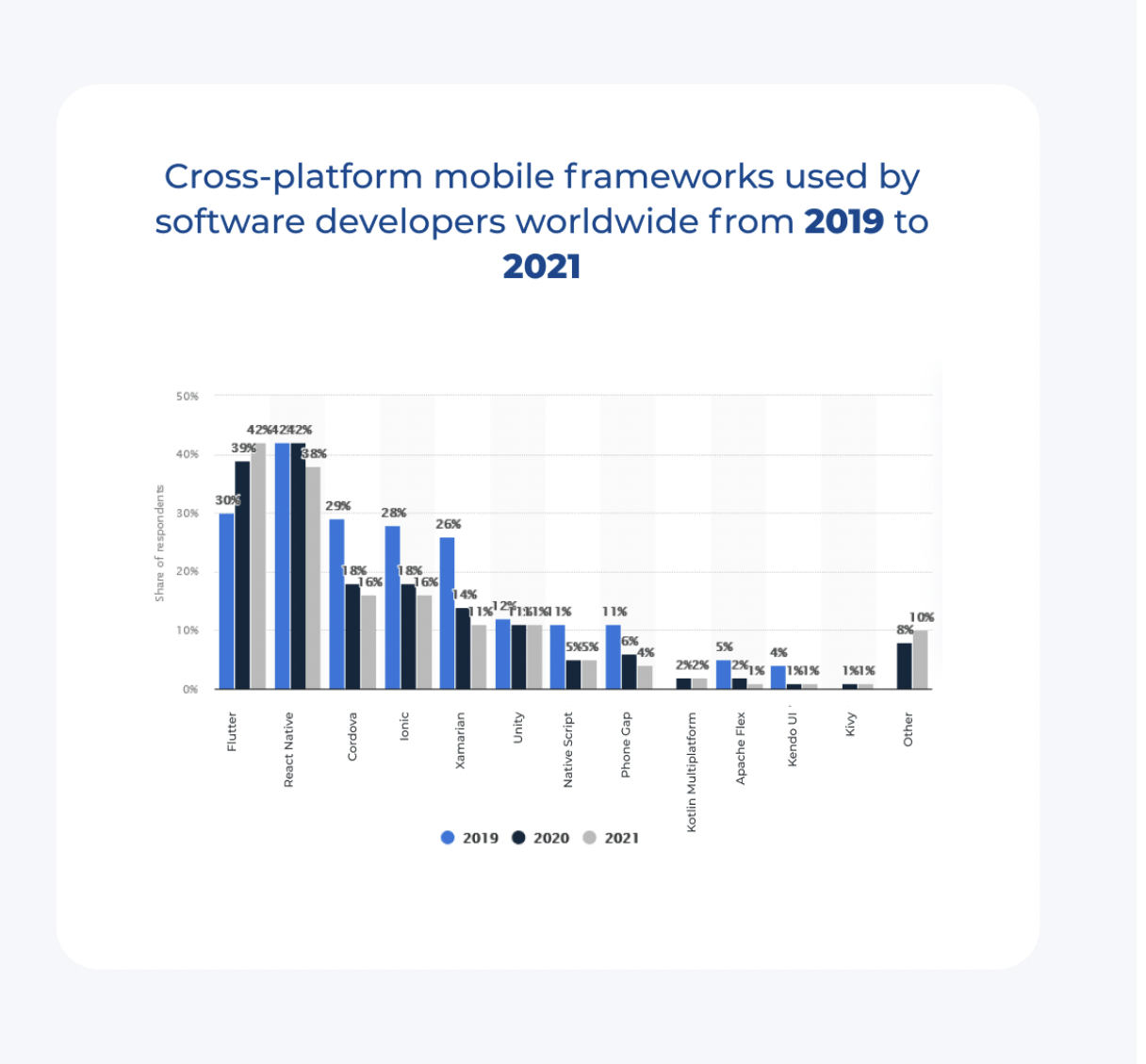
Do you know the top frameworks used for hybrid app development?
The infographic below offers insights into top cross-platform frameworks.
Most hybrid apps are used on mobile devices but can also run on PCs and other web-capable devices. A big reason for developing a hybrid app is portability. It means you can deploy your application quickly without having to do all your coding from scratch.
Advantages of Developing a Hybrid App:
- Lesser cost: One advantage of building a hybrid app is that it helps you save on your development costs. You do not need to hire mobile app developers to develop an iOS app separately from Android. Instead, you need to work with web developers to create an HTML5-based app that can run on both platforms.
- Lesser maintenance cost: Another advantage of developing a hybrid app is that it helps you save on maintenance costs. You need to make only minor changes to both platforms instead of changing several parts separately.
- Highly Scalable: A hybrid app is highly scalable. If you want to add or integrate new features to your app, you will only need to make changes in a single platform instead of two. In addition, its basic structure remains the same irrespective of any additional features.
- Quicker development: The next benefit of developing a hybrid app is that it helps you create an app quicker. Developing a hybrid app enables you to develop an app faster than developing native apps separately. You can build your basic functionality once, thereby saving on development costs by not making it again for every platform. In addition, as your development process requires only minor changes to each additional feature, maintenance is also less tedious.
- Deploy on multiple platforms: Another advantage of developing a hybrid app is that it helps you deploy your app across various platforms. When you choose to build a hybrid app, it does not matter which platform it will be released on first, as all these apps are essentially based on HTML5. Thus, a hybrid mobile app development company in India will be an excellent option if you plan to roll out your app on different mobile platforms like iOS, Android, or Windows Phone.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Mobile App Development:
- The downside is that your app won’t have as many features like a fully developed native app. Still, it will allow users to see what your idea looks like, which could be enough to become interested in investing further time or money into making your concept a reality.
- Most hybrid apps are built using web technologies that render all content text to generate faster on mobile devices. Thus the graphics aren’t nearly as crisp or detailed as those found in native apps.
3) Native vs. Hybrid Mobile Apps: Which one offers a high audience reach?
When deciding whether you should have a native or hybrid mobile app, your primary consideration will be whether your audience uses apps. If they are app users, it’s a no-brainer: go with a native app.
However, if they are not, then creating a native mobile app would be overly expensive and probably ineffective since an audience that does not use apps won’t download one just because it exists. An alternative solution/aspect could be to create a hybrid app.
Although hybrid apps use third-party platforms such as web and HTML5 as their leading technologies, they are available across platforms including Android and iOS like their pure native counterparts.
Who’s the winner: Hybrid mobile apps
4) Hybrid vs. Native Mobile Apps: Which one is a cost-effective solution?
Hybrid app development can create a faster time-to-market and lower costs if your requirements are standard. On the other hand, Native apps require more time and resources for each platform you target but deliver much better performance, increased customer engagement, and improved conversion rates.
If your business is facing trouble managing multiple mobile channels, then hybrid may be the best option to go with at present, while you wait until things settle down to develop only native apps instead.
It also ensures that there won’t be much of an issue with maintaining different versions of an app going forward. It is mainly because newer versions need not necessarily be released simultaneously on every platform you release them on if they were developed using a hybrid technology stack.
Who’s the winner: Hybrid Mobile Apps
5) Native vs. Hybrid Mobile Apps: Which one offers a high user experience?
Whether considering a native or hybrid app, you want to keep a high user experience (UX). UX is how users perceive your app, and it involves a lot more than just how it looks and feels. For example, if a mobile user struggles to interact with your app, UX will take a hit. Companies that create apps for customers should have the design as part of their core competencies or hire someone who does.
It can be hard to find good mobile developers who understand coding and how to make something work great on touchscreen devices and provide a high level of customer satisfaction without added cost since they are more expensive. Native apps offer a more intuitive user experience than hybrid apps because they are written in one programming language and are easier to maintain, troubleshoot, and update.
When you consider that between 60% and 80% of customers abandon mobile sites after just one minute if their needs aren’t met, that makes sense. For example, when you have an issue with your app, like poor navigation speed, you can address it quickly without rebuilding a new version of your app each time.
Who’s the winner: Native Mobile Apps
6) Native vs. Hybrid Mobile Apps: Which one leads to high conversion?
Native mobile apps usually make your customers feel like they are using your company’s actual website, which can be a strong selling point. If you are building a new idea or an app from scratch, you will want to make it on Android’s SDK (Software Development Kit) or iOS’ Swift language.
These options offer excellent user experiences that will help make your app conversion-friendly. Still, there are other benefits to choosing one over another beyond aesthetics and ease of use.
The main advantage of a hybrid app is that one can develop it much faster than a native one. However, two major disadvantages are poor performance and lack of security.
On the other hand, hybrid apps fail to offer high UX and are not as secure as native ones. In addition, some features may not work if you have both a native and a hybrid app in your portfolio.
Final Takeaway:
It’s essential to understand why native applications may be better for some businesses than others. It all comes down to how high an investment you want in mobile marketing and how confident you are in its ability to convert users into paying customers. However, have a look at the following insights from the article.
Hybrid apps are an excellent choice as they offer the following:
- High audience reach,
- A cost-effective option, and
- Lower maintenance cost.
On the other hand, Native apps offer the following:
- High UX and
- A more significant number of conversions.
Choose wisely!