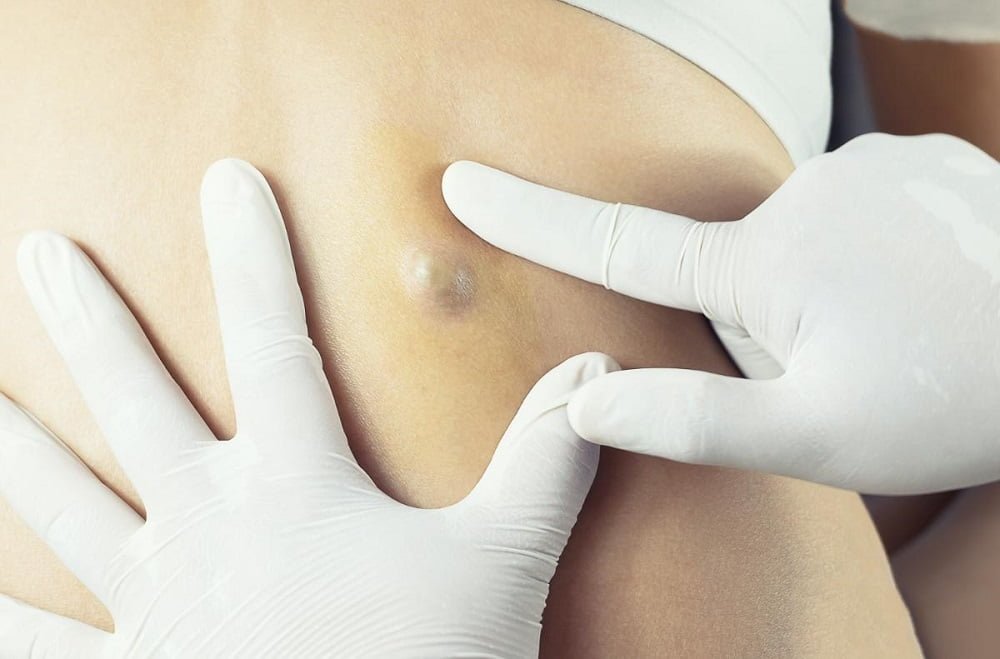
The epidermoid cyst is a cyst that grows on the skin’s surface (epidermis) in most cases. It may also refer to a pillar that extends from a follicle. These terms are often interchangeable. True sebaceous cysts, which grow from the sebaceous, are rare. They are most often associated with a genetic condition called Steatocystoma multiplex.
You most likely already know this condition. This condition occurs in puberty and can produce multiple cysts at once. It is possible to have one sebaceous cyst. It is called steatocystoma basics. The sebaceous cyst may cause cancer-based on the cyst’s size, type, and place.
When it comes to treatment and removal, epidermoid cysts and pilar cysts are functionally identical. These sebaceous are collectively known as cysts. If you think you may have a sebaceous tumor, consult our sebaceous cyst treatment physician in London to talk to a cosmetic physician about treatment options and diagnosis.
How does Sebaceous Cyst Grow?
Your hair, finger, and toenails, as well as your skin, are constantly changing. Skin cells grow at a fantastic rate to replace the old shed cells, and approximately within 27 days, our body changes. A cyst can form from the regenerating cells if they get stuck and collect more cells within themselves. Sometimes, this happens alongside fluid, gas, blood, or pus, which is how an epidermoid cyst looks.
Varieties of elements make up cysts, including keratin. Keratin is the same substance that makes hair, nails, and the other outer body layers, and pilar cysts also contain keratin. True sebaceous cysts, on the other hand, are full of sebum. The sebaceous gland typically secretes this oily substance onto the skin’s surface as a lubricant.
These distinctions aside, all types of cysts are caused by cells failing to function appropriately and trap important substances under the skin rather than releasing them onto the skin’s surface.
Causes of Sebaceous Cyst:
How exactly can this happen? There could be many reasons. Although it is impossible to pinpoint the exact cause, it may be challenging to determine. It does not matter in most cases.
- Injury: Injury to an area could lead to blockages that lead to cysts. Inciting trauma can be anything from scratches and burns to the skin. Sometimes, a cyst may not develop until months later. Surgery can also cause damage to the glands, hair, and skin follicles.
- Condition of Skin: Cysts are known to be caused by acne. Acne, like trauma, can block glands or cause other problems that interfere with normal functioning.
- Hair Follicles: Hair strands can swell when they become infected, inflamed, or inflamed (e.g., folliculitis). Blockages can also occur.
- Deformed hair follicle duct: Sometimes, the follicular conduits connecting sebaceous glands and hair follicles become misshapen or deformed at birth or after trauma. These defects can affect the production of oils by the sebaceous duct.
- Genetic Predisposition: Although it is impossible to inherit a cyst directly, the disease is passed on to children. Gardner’s syndrome can lead to epidermoid cysts and other growths. Basal cell nevus syndrome (basal cell carcinoma) also causes a sebaceous cyst, a form of cancer shortly after puberty.
Symptoms of Sebaceous Cyst:
No matter what causes a cyst, the discomfort will persist. Depending on the type of cyst, a cyst can feel either hard or soft. Sebaceous cysts of all kinds are benign, small, and slow-growing.
Many symptoms accompany cysts, such as a small, crusty spot at the top of the cyst or skin warmth near the cyst. There may be slight differences in the physical appearance of different types of cysts. However, these differences are not significant.
Sebaceous cysts can grow if left untreated. Large cysts can be painful, tender, and uncomfortable, and usually, it depends on the location of a cyst and whether it comes in contact with clothing or other skin.
Sebaceous Cyst Removal Methods:
One can get rid of a cyst with the help of medical treatments, but some people prefer home remedies. Home remedies have a limitation, and it does not work for all types of cysts. Therefore, it is highly recommended to consult with your physician before home remedies.
Medical Treatments For Sebaceous Cyst
A dermatologist can diagnose a cyst and determine if it is cancerous. The procedure involves an examination of the cyst and a review of your medical history. Sometimes, the dermatologist may use an ultrasound to examine the cyst.
A dermatologist may perform a punch biopsy if he suspects that there may be cancer. This involves removing a small amount of the growth and sending it to a pathologist. The dermatologist may remove the cyst entirely if the cyst is noncancerous.
A way of removing a sebaceous cyst
A cyst removal may not be worthwhile if it is small or in a conspicuous location. Sometimes, sebaceous cysts may disappear on their own. Your dermatologist may recommend drainage if your cyst is not too large, but it is in an area that can irritate you by rubbing against your clothing or skin.
You can drain it manually or use a CO2 laser. The presence of a cyst sac increases the likelihood that it will grow back. However, it is also possible that it may not.
The third option is to have the cyst completely removed, and a professional dermatologist or surgeon will remove the cyst. Large cysts can be more painful or uncomfortable because they are significant. Large cysts are less likely to disappear on their own and are more likely to regrow.
There are many ways to remove cysts, but the result is almost always the same.
- Surgical Excision: The dermatologist will numb the area with a scalpel and remove the cyst sac.
- Cryosurgery: In this technique dermatologist, froze the cyst’s liquid nitrogen. It kills the tissue and causes it to fall away.
- Electrosurgery: High-frequency radio waves heat the cyst tissue and kill it.
- Laser-assisted treatment: Cyst removal is performed using a CO2 laser. Approximately one month later, after the cyst wall has shrunk, the physician will remove the entire structure.
Your dermatologist will likely perform a CT scan before performing any of these procedures. It allows your dermatologist to see the cyst better and determine the best way to remove it.
Home Remedies Risks
Like with blisters and zits, many people want to remove unsightly growths as soon as possible. It can be tempting to pull or pinch a cyst until it bursts and seem simple, but it is best to seek medical attention before you try to remove the cyst.
The cyst may recur even if fluid drains. Most likely, the cyst that bursts will also cause an infection. It is riskier to remove your cysts, sacs, and other abnormalities. Also, it requires precision surgical skills.
This precision is essential to avoid serious injury to your skin and surrounding tissues. The risk of infection is also higher. A dermatologist can help you get rid of your cyst. Keep your cyst clear and protected from irritation.
Bottom Line:
Before performing any of these procedures, it is recommended to check with a dermatologist. He will likely do a CT scan to better look at the cyst and determine the best removal method.